
You are about to leave ChooseUltimate.com
This link will open in a new window. Do you wish to continue?
We look forward to serving you. We want your experience with us to be great. We promise to serve and care for you in the same way we would want our family to be treated.
Cardiovascular disease can include a few different diagnoses that affect the circulatory system in different ways. You may have been diagnosed with:
Each of these diagnoses can impact your quality of life. By understanding the unique symptoms, treatments, and methods to manage these diseases, you can greatly improve your outcomes and meet your personal goals.
A heart arrhythmia is a heartbeat that has an irregular rhythm. The heartbeat can be too fast, too slow, or out of sync. Some people have no symptoms with heart arrhythmia. But some could experience any of the following symptoms:
Ventricular Fibrillation is a serious arrhythmia that can cause the blood pressure to drop dramatically, collapse, and breathing and heart rate to stop. This is an emergency that requires 911 and CPR.

Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial Fibrillation impacts over 6 million people in the United States and is most common in people over 60 years old. (8) Atrial Fibrillation causes the heart to beat rapidly and out of rhythm. When this happens, blood can pool in the heart increasing the risk of clot formations. Clot formations can travel through the body from the heart leading to stroke. This is why blood thinners are a critical treatment for anyone with a diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation.
Treatment for Atrial Fibrillation includes medication to address clot formations and control heart rate, therapy to reset the rhythm of the heart known as cardioversion, and possible other interventional cardiac procedures. (8)
Sick Sinus Syndrome
Sick Sinus Syndrome can create episodes of low heart rate, pauses, and irregular heartbeats. (6) When the heart rate stays low you can experience symptoms that include fainting or near fainting, shortness of breath, severe fatigue, confusion, chest discomfort, and palpitations.
Sick Sinus Syndrome can lead to other arrythmias like Atrial Fibrillation and to complications like heart failure, cardiac arrest, and stroke. (6) This is why treating sick sinus syndrome is important. Treatment options depend on your assessment and can include: (6)
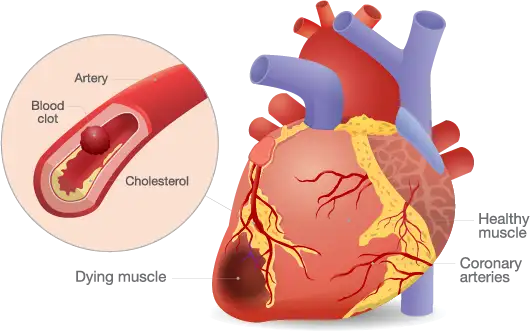
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition that affects the main blood vessels that supply oxygen to the heart. These blood vessels narrow due to plaque (debris of fat, cholesterol, blood contents, etc.) on the artery walls. (3) This is known as atherosclerosis, the primary cause of coronary artery disease. (3)
Symptoms of coronary artery disease include chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Coronary artery disease chest pain can feel like squeezing, tightness, or heaviness on the chest. This type of chest pain is often called angina. Angina can feel different for men and women. Women may experience angina pain in their neck, arm, or back. (3)
Coronary artery disease can lead to a heart attack. This will happen when the disease completely blocks an artery wall. Some common symptoms of a heart attack could include: (3)

If you think you are having a heart attack, call 911 immediately!
In some people, none of these symptoms occur when having a heart attack. Symptoms could be very mild. This is why it is important to know your risk factors and regularly see your doctor. The risk factors for having a heart attack include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, being overweight, and having a family history.
Talk to your doctor about your risk factors and what you can do to prevent cardiac disease.
Medical management of coronary artery disease can include a variety of treatments based on your doctor’s assessment and your symptoms. Some common treatment options can include: (3)
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) is a disorder where the blood vessels narrow, spasm, or get blocked leading to decreased blood flow. (2) PVD is most commonly caused by atherosclerosis which allows for the buildup of plaque inside the artery walls. When plaque is present, narrowing and blockages occur leading to decreased circulation. (2) People who have coronary artery disease will often have peripheral vascular disease as well. (2)
Peripheral vascular disease can have a wide range of symptoms depending on what part of the body it is affecting. Many of the symptoms can be seen in parts furthest from the heart like the legs. Some common symptoms include: (2)
Medical management of peripheral vascular disease can include a variety of treatments based on your doctor’s assessment and your symptoms. Some common treatment options can include: (2)
This is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein. This is a serious condition because the blood clot can move to the lung causing a life-threatening condition known as Pulmonary Embolism requiring emergency medical care. (7) Common signs and symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis are swelling, redness, and pain to the area. (7) The signs of a pulmonary embolus include sudden onset shortness of breath and chest pain requiring immediate medical care! (7)
Medical management of deep vein thrombosis can include treatments based on your doctor’s assessment and your symptoms. Some common treatment options can include: (7)
There are many things that can be done to prevent the formation of clots. Some self-management activities include: (7)
Hypertension is known as high blood pressure. High blood pressure greatly affects your heart by making it harder to pump blood. (5) High blood pressure may not have any signs or symptoms. This is why it is important to keep appointments with your doctor and know your blood pressure numbers.
According to the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association, the ideal blood pressure is lower than 120/80 (systolic number/diastolic number). (5) If your blood pressure number is higher than 130 systolic (the top number) or higher than 80 diastolic (the bottom number) your doctor can diagnose you with hypertension. (5)
If blood pressure gets very high, it can be an emergency. Any blood pressure that is 180 systolic (the top number) or 120 diastolic (the bottom number) needs emergency medical attention.
Elevated blood pressure that is left untreated can put you at risk for a heart attack, stroke, and other serious health ailments. This is why it is very important to check with your doctor and know your numbers (5).
There are many things people can do to keep their blood pressure in a healthy range. Some common self-management activities include: (5)

A low sodium diet limits salt intake. Salt has an immediate impact on your heart’s ability to pump. Salt makes it harder for your heart to pump the extra fluids in your body. Removing excess salt from your diet can improve shortness of breath when there is too much fluid buildup in the body.
Educate yourself on the salt in your diet. Many foods have hidden salt that can negatively impact your condition. Click here for more information on a healthy heart diet that limits excess salt. (1)
Understanding your diagnosis can provide you with information to make the best decisions for your health and quality of life. Here are some suggestions to ask your doctor with your next visit: