
You are about to leave ChooseUltimate.com
This link will open in a new window. Do you wish to continue?
We look forward to serving you. We want your experience with us to be great. We promise to serve and care for you in the same way we would want our family to be treated.
Chronic Lung Disease can include a few different diagnoses that affect the lungs in different ways. You may have been diagnosed with:
Each of these diagnoses can impact your quality of life. By understanding the unique symptoms, treatments, and methods to manage these diseases, you can greatly improve your outcomes and meet your personal goals.
Asthma is a chronic disease that makes it hard to breathe by narrowing and swelling your airway and producing extra secretions. It is common to hear wheezing with asthma with difficulty breathing. Asthma can come on quickly and vary in severity from minor discomfort to a life-threatening attack requiring emergency intervention. (4)
Although asthma cannot be cured, understanding triggers, taking prescribed medications, and working with your doctors closely can greatly improve asthma management. (4)

COPD is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. This disease makes it difficult to breathe due to chronic inflammation in the lungs blocking airflow. It is common to have difficulty breathing, have a cough with mucus, and have wheezing. Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis are the two main causes of airway blockage in COPD. (5)
Emphysema occurs when the tiny branches of the lungs are damaged due to exposure to lung irritants like smoke. (5) Chronic Bronchitis occurs when the branches of the airway that carry air to the lungs become inflamed and lined with mucus making it difficult to breathe. (5) The combination of Emphysema and Chronic Bronchitis greatly impacts a person’s ability to breathe.
Having COPD can increase your risk of the following: (5)
Medical management of COPD can include a variety of treatments based on your doctor’s assessment and your symptoms. Some common treatment options can include: (5)
Pulmonary Fibrosis is a lung disease that causes inflammation and scarring to the tiny air sacs in the lungs. The thickened, stiff lung tissue makes it hard for the lungs to take in oxygen. (6) In addition to shortness of breath, dry cough, and fatigue, pulmonary fibrosis symptoms can include unintended weight loss, muscle and joint aching, and rounding of the fingers and toes called clubbing. (6)
Medical management of Pulmonary Fibrosis can include a variety of treatments based on your doctor’s assessment and your symptoms. Some common treatment options can include: (6)
Pulmonary hypertension can have unique symptoms that include: (7)
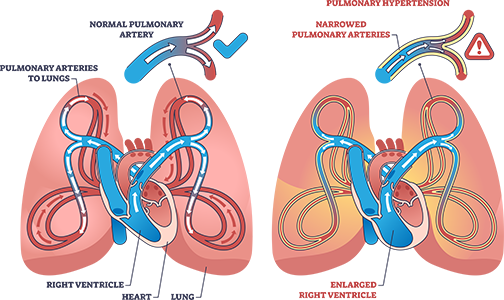
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure that specifically targets the arteries in your lungs and heart. The blood vessels can narrow or become blocked affecting the blood flow through the lungs. This can make the heart work harder to circulate blood. The heart can begin to become weaker over time due to this condition. (7)
Medical management of Pulmonary Hypertension can include a variety of treatments based on your doctor’s assessment and your symptoms. Some common treatment options can include: (7)
A low sodium diet limits salt intake. Excess salt can cause fluid retention in your body. This has an immediate impact on your heart’s ability to pump. Salt makes it harder for your heart to pump the extra fluids in your body. Removing excess salt from your diet can improve shortness of breath by reducing the fluid buildup in the body.
Educate yourself on the salt in your diet. Many foods have hidden salt that can negatively impact your condition. Click here for more information on a healthy heart diet that limits excess salt. (1)
Specific breathing techniques can greatly manage the shortness of breath that occurs with COPD.
To perform pursed lip breathing practice the following steps:
When you practice pursed lip breathing you control your shortness of breath by breathing slowly and deeply. This technique also releases trapped air helping you take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide more efficiently.
Plan
Stay Organized
Keep it Simple

Some common examples of energy conservation that can positively impact your day:
Understanding your diagnosis can provide you with information to make the best decisions for your health and quality of life. Here are some suggestions to ask your doctor with your next visit: